What is a Star?
A star is a luminous ball of gas, mostly hydrogen and helium, held together by its own gravity. Nuclear fusion reactions in its core support the star against gravity and produce photons and heat, as well as small amounts of heavier elements. The Sun is the closest star to Earth.
A star is a luminous sphere of plasma held together by its own gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Other stars are visible from Earth during the night, appearing as a multitude of fixed luminous points in the sky due to their immense distance from Earth.
Historically, the most prominent stars were grouped into constellations and asterisms, and the brightest stars gained proper names.
Knowing More About Stars
You can tell the different characteristics of a star by observing certain characteristics such as their magnitude, their color, and their sizes.
A star's magnitude describes how bright the star is.
Brightness of stars is assigned a number starting with the brightest star starting at about -1 magnitude. Dimmer stars are zero or positive numbers. The larger the number means the dimmer the star is. For example, a star -1 magnitude is brighter than a star 0 magnitude. A star 0 magnitude is brighter than a star 1 magnitude. A star 1 magnitude is brighter than a star 2 magnitude. A star 4 magnitude is brighter than a star 5 magnitude. Magnitude sequence for stars starting with the brightest is -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 magnitude, ... etc.
Color
As you may or may not know, stars actually come in a variety of colors. But do you know all of the different colors that stars can be?
We will explore why stars come in different colors and then we will identify all of the different colors that stars can be.
· The color that a star appears depends mainly on the temperature that it burns at. More specifically, the color is directly related to the surface temperature of a star. In the lowest temperature range, stars appear in the red color family. At the highest temperatures, stars appear blue. In general, stars are categorized by certain types depending on their temperature, and those temperature ranges and types are as follows:
·
o 3,000° – 6,000° Fahrenheit (1,649° – 3,316° Celsius): Type M
o 6,000° – 8,500° Fahrenheit (3,316° – 4,704° Celsius): Type K
o 8,500° – 10,500° Fahrenheit (4,704° – 5,816° Celsius): Type G
o 10,500° – 13,000° Fahrenheit (5,816° – 7,204° Celsius): Type F
o 13,000° – 17,500° Fahrenheit (7,204° – 9,704° Celsius): Type A
o 17,500° – 50,000° Fahrenheit (9,704° – 27,760° Celsius): Type B
o 50,000° – 100,000° Fahrenheit (27,760° – 55,538° Celsius): Type O
Now that you know what the different classifications for star temperatures are, the next question is what color are stars of a given temperature. The following star color list shows what color a star will be given the type (i.e. the temperature range) it falls under:
o Type M stars: Red
o Type K stars: Orange
o Type G stars: Yellow-White
o Type F stars: White
o Type A stars: White
o Type B stars: Blue-White
o Type O stars: Blue
There are seven classes of stars according to their color.
The temperature that corresponds with these stars are based on the electromagnetic spectrum.
The temperature increases as the color gets darker.
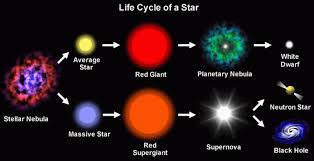
Star Life Cycle
· Stars are formed in clouds of gas and dust, known as nebulae. Nuclear reactions at the centre (or core) of stars provides enough energy to make them shine brightly for many years. The exact lifetime of a star depends very much on its size. Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars and may only last a few hundred thousand years. Smaller stars, however, will last for several billion years, because they burn their fuel much more slowly.
Eventually, however, the hydrogen fuel that powers the nuclear reactions within stars will begin to run out, and they will enter the final phases of their lifetime. Over time, they will expand, cool and change colour to become red giants. The path they follow beyond that depends on the mass of the star.
· Small stars, like the Sun, will undergo a relatively peaceful and beautiful death that sees them pass through a planetary nebula phase to become a white dwarf. Massive stars, on the other hand, will experience a most energetic and violent end, which will see their remains scattered about the cosmos in a enormous explosion, called a supernova. Once the dust clears, the only thing remaining will be a rapidly spinning neutron stars, or possibly even a black hole.
Types of Stars
The life of a star is inversely proportional to its size. Massive stars will die first because they consume fuel faster than small stars. This is why most of the massive stars last only for thousands of years, as compared with the average stars that can live up to millions of years.
All About Constellations
What are Constellations?
Constellations
are patterns in the night sky often formed by the most prominent stars to the
naked eye. Technically a constellation defines not just the group of stars that
form their patterns but also the region of sky in which it rests.
There are 88
constellations across the sky between the northern and southern hemispheres
and, in both these parts of the celestial sphere, these patterns of stars
differ. The current list, which includes constellations such as Orion,
Cassiopeia, Taurus and the Plough, has been recognised by the International
Astronomical Union (IAU) since around 1922 and are based on the 48 which were
previously identified by Greek astronomer Claudius Ptolemy.
Constellations often
carry names and take the shape of gods, hunters, princesses, objects and
mythical beasts associated with Greek mythology – however, at times, it
requires quite an imagination to draw out what some constellations are supposed
to represent! Some of the most obvious stars in a constellation are often given
names and in general, the most visible stars of each constellation are assigned
Greek letters with the brightest taking on the first letter of the greek
alphabet (alpha), the second brightest taking beta and so on. As an example,
the brightest star in Lyra is Vega which is also called alpha Lyrae.
Circumpolar Constellations
Because of the rotation
of the Earth and its orbit around the Sun, we divide the stars and
constellations into two groups. Some stars and constellations never rise nor
set, and they are called circumpolar. All the rest are divided into seasonal
stars and constellations. Which stars and constellations will be circumpolar
and which seasonal depends on your latitude. In the northern hemisphere, we
will always be able to see stars and constellations in the the northern
circumpolar sky, while in the southern hemisphere, we will always be able to
see stars and constellations in the southern circumpolar sky.
Northern Circumpolar Constellations
Constellations
in the northern circumpolar sky include Auriga,
Camelopardalis, Cassiopeia, Cepheus, Draco, Lynx,
Perseus, Ursa Major, and Ursa Minor. These constellations are always
visible in the night sky of the Northern Hemisphere.
Southern Circumpolar Constellations
Constellations
in the southern circumpolar sky include Grus, Phoenix, Indus, Tucana, Pavo,
Ara, Eridanus, Hydrus, Horologium, Reticulum, Octans, Apus, Triangulum
Australe, Lupus, Circinus, Musca, Crux, Centaurus,Carina, Vela,
Puppis, Dorado, and Chamaeleon. These constellations are always visible in the
night sky of the Southern Hemisphere.
Astrology
And because of
constellations "zodiac signs" were formed.
The different
astrological signs and their corresponding dates.
For more facts and
informations about constellations, click All About Constellations.
And for fun quizzes and
games, click Fun Brain All About Constellations.
Reflection
Stars and Constellations
are one of my favorite topics in Science. Ever since I was young I am already
interested in stars especially when I try to connect it and I never knew that
whenever I'm connecting the stars it is already called constellations. I found
stars and constellations easy to understand because I am so interested about
the topic. Discovering and exploring more about stars and constellations, it is
so interesting because when you read the history behind those topics you'll be
amazed on how stars are formed, their life cyle and many more. I
discovered more about stars and constellations like, the sun is one of our
stars, that massive stars last only for thousands of years and many more. I
would like to expound more next time and tackle about the things that I haven't
tackled here on my blog.
"Don't wait for the stars to align. Reach up. Rearrange them
the way you want them to be. Create your own constellation" - Pharrel
Williams